ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) is an important protocol used in computer networks. Its purpose is to find the MAC address of a device using its IP address, so that data can be delivered correctly within a local network (LAN).
IP addresses are logical, while MAC addresses are physical. Since network communication happens based on MAC addresses, ARP is required to map IP → MAC.
Why ARP Is Important
Think of it like this:
- IP Address = Name of a person
- MAC Address = The exact home / location of that person
To deliver data correctly, the device needs the exact MAC address.
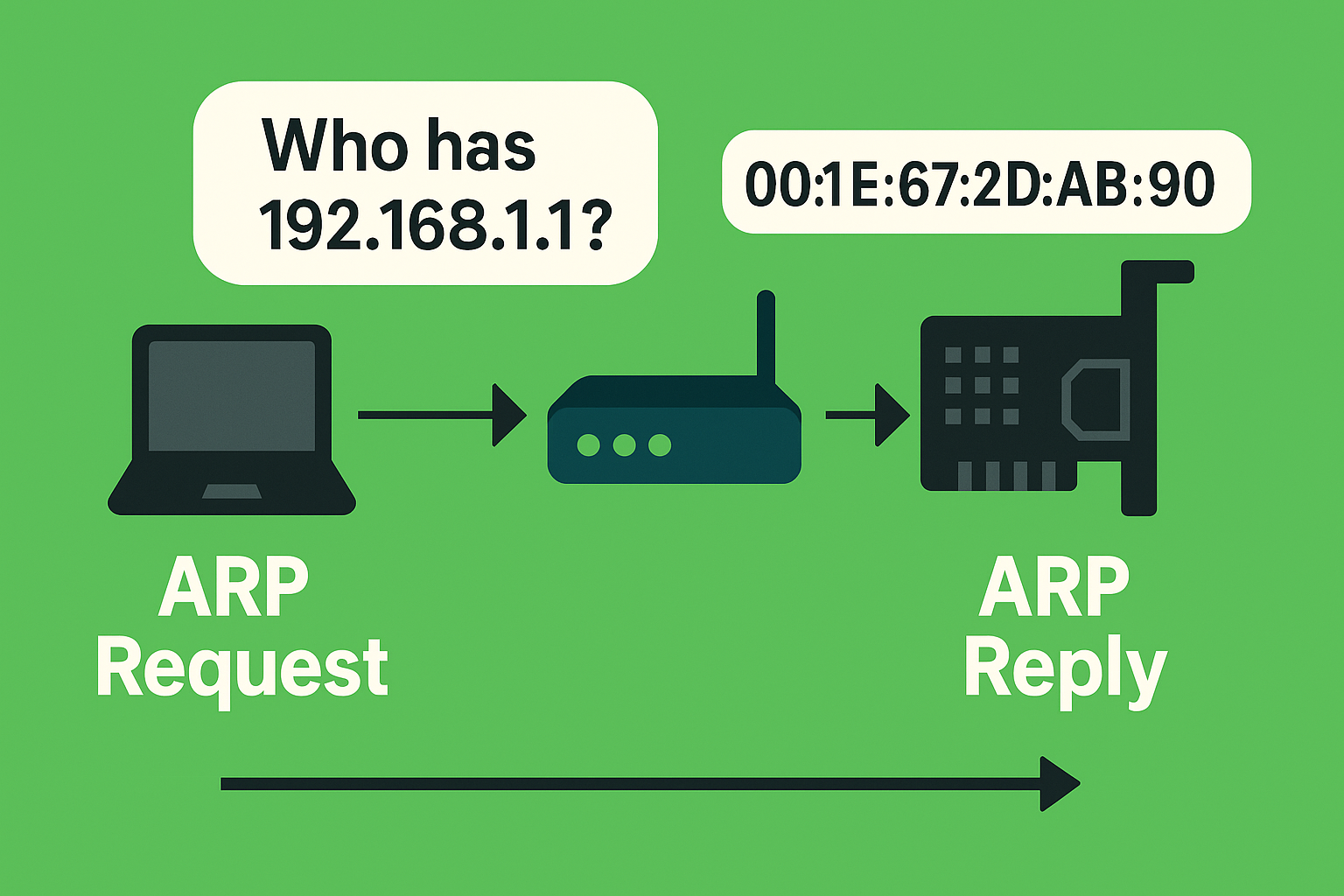
How ARP Works (Simple Explanation)
- A device wants to send data to another IP address.
- But it does not know the MAC address of that IP.
- So it broadcasts a message to the entire network:
“Who has this IP? Please send me your MAC.” - The device with that IP replies:
“This is my MAC address.” - The sender stores this information in its ARP Table for future use.
What Is the ARP Table?
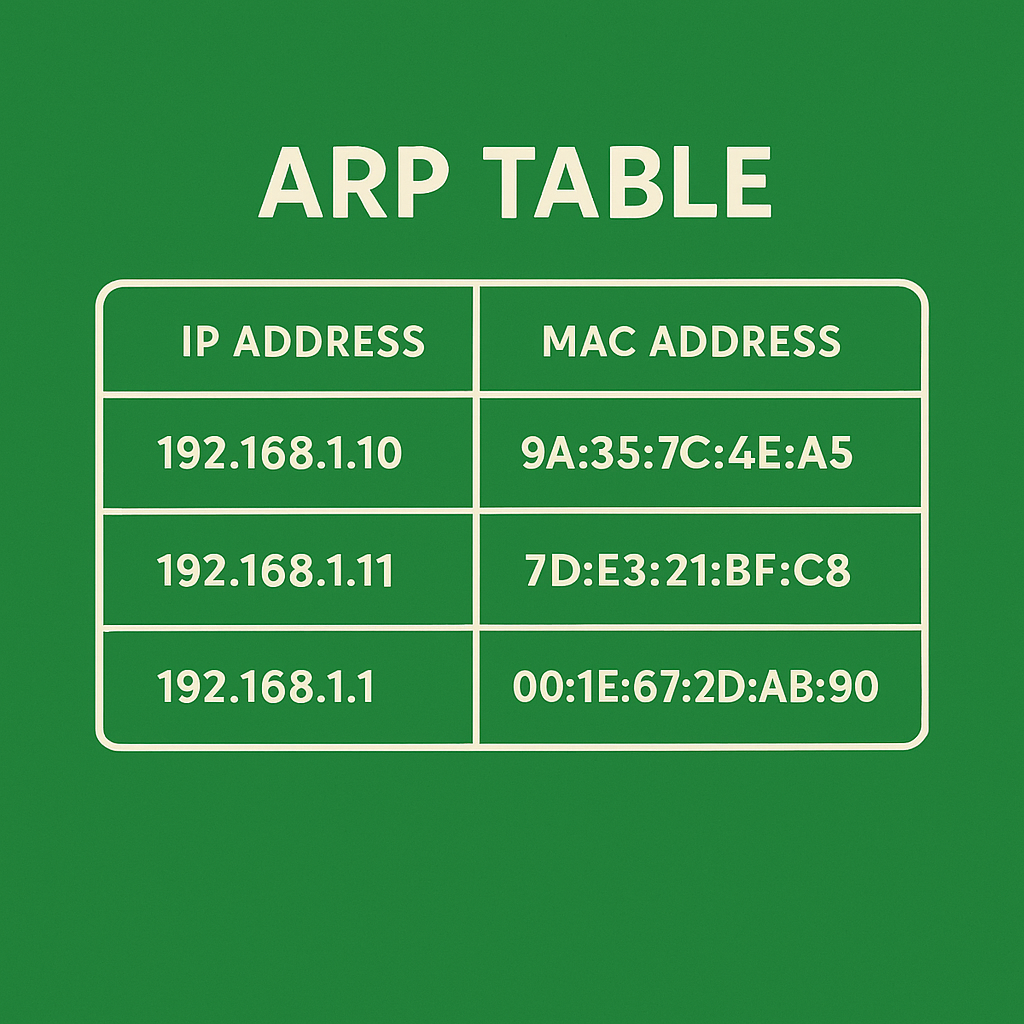
The ARP table is a small list stored in the device’s memory that contains IP → MAC mappings.
How to View ARP Table
# On Windows
arp -a
# On Linux / Mac
ip neigh show
What Is ARP Spoofing? (Man-in-the-Middle Basics)
ARP does not verify whether responses are real or fake. It trusts devices blindly.
An attacker takes advantage of this.
The attacker sends fake ARP replies in the network claiming:
“This IP belongs to me.”
This allows the attacker to position themselves between the victim and the router.
This is known as a:
MITM (Man-in-the-Middle Attack)
What Can Happen During ARP Spoofing?
- Attacker can capture network data
- Login credentials may be exposed (if traffic is not encrypted)
- Victim may be redirected to fake websites
- Network performance may slow or break
How to Detect ARP Spoofing
- ARP table shows the same IP address changing MAC repeatedly
- Duplicate IP warnings appear
- Network suddenly becomes slow
- Network scanning tools show suspicious ARP replies
How to Prevent ARP Spoofing
- Use VLANs / Network Segmentation to separate devices
- Enable Dynamic ARP Inspection (DAI) on managed switches
- Enable DHCP Snooping for verifying source of ARP messages
- Use HTTPS, SSH, TLS encryption to secure data
- Use Static ARP Entries only on critical systems
Conclusion
ARP is a simple but essential protocol for communication inside local networks. Understanding ARP helps in understanding network attacks like MITM, packet sniffing, and spoofing.
Awareness is the first step to defense in cybersecurity.